Marketing Theory Lecture
1.0 Definition of Marketing
Marketing is often thought to be just about advertising or selling, which is not the case. It is a management process that ensures businesses can interpret consumer needs and match or exceed them while making profit. Marketing is an exchange process through which companies satisfy existing and potential consumer needs by creating and offering goods or services with some added value. Marketing ensures organisations have a better chance of profitably carrying out their business activities by matching what they are offering with the customer’s needs. In other words, as opposed to the popular views, marketing considerably focuses on product demand development and consumer satisfaction.
State at least ten products and services that you became aware of because of marketing carried out by its producer.
Hint: Marketing can include activities such as sales promotion, door to door selling, publicity stunts, branding, packaging and advertisements.
Case study
Coke Studio Africa is an initiative by Coca-Cola that brings together various musicians across Africa for a given period so that they can perform live to an audience in a specially designed studio. The initiative is geared towards emotionally connecting customers to its products, which in turn will lead to increased brand loyalty. Through the coke studio initiative, Coca-Cola has driven up the demand for its products, which consumers find highly satisfying.
2.0 Importance of Marketing to Contemporary Businesses
Marketing is crucial for the survival and continuity of business. This is because businesses achieve their business goals through marketing as it enables them to determine consumer needs, satisfy the needs, target the right customers, stay ahead of competitors and enhance their profitability.
One of the most important functions of marketing is to create awareness about products and services to potential customers and increase consumer loyalty. Through marketing, customers become knowledgeable of what a firm is offering and on the other hand, businesses use the opportunity to convince these consumers to buy their products or seek their services. Thus, marketing gives an organisation the opportunity to be discovered by prospective customers. An example of a company who continuously utilise successful marketing is Coca-Cola. Coca-Cola consistently utilise aggressive marketing campaigns across multiple platforms to increase customer awareness of its full range of beverages.
Marketing enables organisations to increase and/or retain market shares and retain their loyal consumers as well as attracting new customers through the development of long-term strategic relationships with customers. Increased market share results in more sales for businesses because the involved firm’s market reach is high and customers are more likely to buy products and services from firms that have a large market following. When loyal customers inform friends and family about the products of their organisation, the sales progressively grow, and customers trust an organisation more.
Need Help With Your Business Studies?
If you need assistance writing a business report, our academic report writing service can provide valuable assistance.
See how our Report Writing Service can help today!
Marketing also helps strengthen a company’s reputation through brand building. An organisation’s participation in community activities and programmes, effective public communication and relations together with quality products and services supported by marketing serve to enhance the corporation’s reputation. Good marketing strategies can influence how potential and existing customers position a firm in their minds. For example, Apple is the leading seller of smartphones because, in the last decade, it has consistently launched products of unmatched quality.
Marketing also fosters healthy competition in the market environment. Marketing enables small and new businesses to enter a market and compete with well-established companies through aggressive product awareness and pricing strategies. Marketing makes rival businesses knowledgeable about each other’s strategies. In turn, such information compels businesses to modify their approaches to win targeted consumers, for instance, through developing competitive price packages.
Apart from prices, marketing also provides highly relevant information to firms such as the demand levels, successes and failures of products in the market. For instance, competition between Coca-Cola and Pepsi has maintained the companies’ product prices and led to the development of innovative products, for instance, Diet Coke, a soft drink targeting health-conscious consumers, among others.
Case study
Microsoft Corporation that produces computer operating systems delivers a new operating system into the market named Windows 10. However, consumers have a problem downloading and using the new Windows system and thus end up poorly reviewing and rating the new operating system. The negative publicity from unsatisfied consumers causes the computing technology giant to lose a significant market share.
What can Microsoft do in terms of marketing to regain the market share that it once held? State how the marketing activities it will carry out will be important to achieving its marketing goals.
Can you also think of organisations that face similar market situations with Microsoft and explain how marketing helped it overcome the challenges it was facing?
3.0 Marketing Theories
Marketing management involves numerous ideas and theories on how businesses should carry out their marketing activities. The theories' usability and application are dependent on the prevailing market situation, as will be discussed in this chapter.
The commonly used theory in the development of marketing business strategies is the Ansoff matrix. Besides being simple, the matrix visualises the current strategic position of an organisation and offers possible alternatives that could be employed. The only shortcoming of the Ansoff matrix is that it does not consider external factors that affect marketing such as unprecedented market changes or resource unavailability and hence cannot be used singlehandedly.
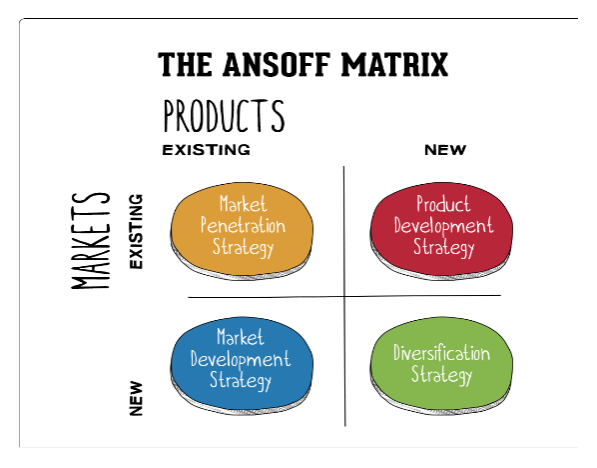
Figure 1 - Ansoff’s Matrix Illustrated
The PESTLE and SWOT analysis are also suitable methods of identifying marketing opportunities and therefore, can be used alongside the Ansoff Matrix to develop a marketing strategy. A PESTLE analysis is used to analyse and gain knowledge of the external environment in which a business operates using the headings as illustrated in the below figure (figure 2). Conversely, a SWOT analysis is an internal investigation of a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
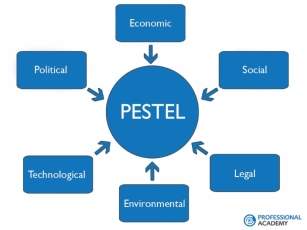
Figure 2 - PESTLE Analysis Illustrated
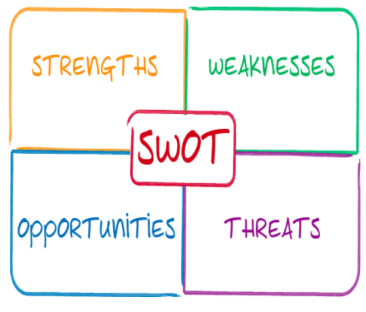
Figure 3 - SWOT Analysis Illustrated
However, there is also the BCG (Boston-Consulting-Group) model that measures a company’s strength in a relevant market segment is much more flexible than the SWOT and PESTLE analyses and especially when employed alongside the GEM (General-Electric-Matrix) in identifying the possible opportunities and problems facing given products in the market.
Despite the correlation between BCG and GEM, the two differ on how they define business units. In the BCG matrix, only products are measured against the industry’s attractiveness scale, and on the other hand, in GEM, business units can be products, product lines, a service or even a brand.
Apple deals in a wide range of products from desktops, tablets, smartphones and watches. The GE matrix has helped Apple and other similar organisations to evaluate the business units that need further investment, development or divestiture.
In addition, Booms and Bitner recommend the use of the 7Ps marketing mix (people, process, physical evidence, place, price, promotion and product) by marketers to determine the type of product or brand a business can offer to its customers. The 7Ps approach is a cost-effective method of identifying marketing opportunities and makes it easier for businesses to adapt to the dynamic marketing environment than most of the other marketing theories.
Think of hypothetical business situations that the Ansoff matrix marketing theory is most suitable for solving.
Hint: Remember, the Ansoff matrix is broken down into four marketing strategic options that include MP (Market-Penetration), PDev (Product-Development), MD (Market-Development) and PDiv (Product-Diversification).
Now, can you think of an actual example of a business that has applied the Ansoff matrix marketing theory in the four phases? State the marketing activities the business you have identified above applied when adopting the Ansoff matrix theory
Highlight three advantages of using the BCG and GE matrix combination over a PESTLE and SWOT analysis combination
Think of hypothetical market situations that may necessitate organisations to use the BCG and GE matrices in evaluating their product portfolio
Hint: a product portfolio is an array of products and services provided by an individual company
Now, can you think of at least five currently operational businesses that may find the BCG and GE matrices combination useful in managing their business units?
Hint: a business unit can be a product, service or line of goods
4.0 Advertising Campaigns
An advertising campaign involves strategic messages placed in multiple media channels at fixed times. The messages have a single campaign theme, which is the central message communicated through such promotions. Advertising campaigns aim at achieving goals such as brand establishment, raising brand awareness and increasing sales. In this section, the factors to consider when creating a successful campaign strategy along with the different types of marketing strategies adopted by businesses will be extensively discussed.
Nike’s Just Do It advertising campaign is one of the most successful marketing campaigns in the world together with Coca-Cola’s Christmas campaign that reinvented the Santa Claus image.
Quiz:
What effect has Coca-Cola’s consistent marketing campaigns had on its brand awareness and sales globally?
State other five successful global advertising campaigns
4.1 Fundamentals for Building a Good Advertising Campaign Strategy
4.1.1 Setting the advertising objective
Marketing campaigns help organisations achieve their marketing goals. Some of the objectives include brand awareness, creating interest, providing information, stimulating demand and brand strengthening.
A business should set realistic and achievable advertising campaign goals. A well-crafted advertising campaign that has a strong message targeting a given population can be used to achieve some of the aims mentioned above. For example, to increase consumer’s interest, an organisation should mention the features and benefits of existing as well as future products.
4.1.2 Setting the advertising budget
Proper planning and allocation of an organisation’s resources such as personnel and funds enable it achieve its advertising campaign’s objectives. Running advertisement campaigns can be quite costly to an organisation; hence the need to make adequate plans on how the funds are to be spent during marketing.
Quiz:
What is the cheapest media channel through which an organisation can carry out its advertising campaign?
Hint: (the internet, television, radio, social media)
Businesses could use numerous methods to develop cost-effective advertising budgets. A commonly employed technique is setting the advertising cost as a percentage of either previous sales or forecasted sales (Hise, 2013).
Quiz:
Which is the better method of setting a budget constraint between using the percentage of previous and forecasted sales? Which is more realistic?
Promotional activities can be run as planned and over the intended period of the marketing campaign if budgeting is done properly.
4.1.3 Selecting media channels for message delivery
With the objectives and budget already agreed on, an organisation now focuses on the media outlet that it will use in delivering the advertising campaign’s message.
Media channels have a significant influence on the type of message to be created and its frequency of delivery. Businesses can incorporate both traditional (radio and television) and modern media (the internet and mobile devices) channels to pass messages to their target audience. The use of the right media channel will enable companies to reach their intended customers quickly and affordably. The chosen media outlet should deliver multi-sensory advertisements and messages that have both visual and audio appeal (Hultén, 2011).
For example, you are a marketing manager at a medium- sized company that specialises in the production of wood pellets used in cooking. The marketing function is deliberating on how to aggressively market the wood pellets. The target market is composed of people residing in rural areas. What kind of media channel would you consider to use in reaching your intended audience?
Hint: the sensory experience you want your prospects to have greatly determines the type of media channel to use.
The market reach of a media channel should also be considered, together with the cost of placing an advertisement. Another factor is advertising clutter where media outlets include many advertisements within a limited space and time. Advertising clutter forces businesses to increase the frequency of their ads, which in the long run, increases their expenses. Making a well-informed selection of a media outlet will help an organisation achieve its marketing campaign objectives.
Compare and contrast the traditional and contemporary media channels in terms of market reach, the cost of advertisement and advertising clutter.
Hint: television and radio versus the internet and mobile phones
What media channel would you advise a conglomerate such as Coca-Cola to use in reaching a target audience that is majorly in remote areas?
Hint: able to reach a mass audience
4.1.4 Creating an advertisement message
An advertising campaign is composed of many promotional activities that are tailored to fit into the message an organisation is sending to its target population. To create an effective message, businesses must take into consideration factors such as the characteristics of the target audience, the media outlet being used, products and general advertising objectives.
Firms need to research well on the make-up of its intended audience when making the message content. Additionally, the target audience’s knowledge about a product affects the contents of a message. For example, new products will have a message different to that of popular products.
Quiz:
Think of an advertising campaign in your locality that was declared unfit for consumption by the governing authority citing it as inappropriate for certain members of the population
Hint: explicit content, violence encouragement and downgrading of family values
A consideration of these factors together with the general objectives of the advertising campaign will help an organisation craft a message that is effective in achieving its marketing goals.
Overall, through the marketing process, a business establishes a suitable slogan (word or phrase), value proposition (reason for customers to be interested in a product) and appeal (emotional, use of fear, humorous or sexual) for its intended market.
Quiz:
State five advertising campaign messages and categorise them as either using an emotional, fear or sexual appeal to capture the audiences’ attention.
Case study
Coca-Cola Company recently came up with an advertising campaign which involved the printing of names on soda cans. The goal of this initiative is for friends and family to find a can with the matching name of the person they would like to share the beverage with. Can you identify the types of appeal the company utilised in its effort to capture the attention of its potential and existing customers?
4.1.5 Evaluating advertising campaign results
The evaluation of promotional activities is crucial to ensuring the success of an advertising campaign. Continuous assessment enables businesses to identify opportunities and threats facing the success of marketing campaigns allowing organisations to develop measures that ensure advertising campaigns achieve set marketing targets.
To evaluate a campaign’s success, the results of the process are compared against its set objectives. For example, when the objective is to improve brand awareness, a successful campaign will measure the number of people made aware of the brand at the end of the advertising campaign.
Evaluation and monitoring are of great use if a company sets realistic, measurable and achievable advertising campaign objectives.
What is your example of realistic advertising campaign objectives?
4.2 Marketing Strategies
A marketing strategy refers to the way marketing activities are planned, together with the allocation of resources to involved activities. These strategies are modelled with the aim of ensuring that marketing goals and the overall business objectives are achieved. Companies use the marketing mix, which is a combination of product, price, place and promotion, to develop and test a marketing strategy.
4.2.1 Types of marketing strategies
Marketing strategies adopted by businesses vary widely depending on factors such as cost, marketing objectives, the intended market and other unique marketing situations. In this section, different kinds of marketing strategies will be compared with and contrasted against each other.
Mass marketing and guerrilla marketing strategies are cheaper and appeal to larger audiences (Nufer, 2013) than direct marketing strategy. Similarly, the viral marketing strategy, which involves the use of social networking services and word of mouth has a strong linkage with mass marketing and online marketing strategies.
Quiz:
When is the mass marketing strategy appropriate to market an organisation’s product?
State at least five products that cannot be mass marketed and explain why?
Viral marketing strategy, when used alongside mass marketing and guerrilla marketing strategies has often been recommended as a suitable marketing strategy for increasing brand awareness (Nufer, 2013). Furthermore, using the three of them together could potentially reach a vast number of both prospective and existing customers while not being a financial burden to businesses.
Coca-Cola has used guerrilla marketing previously to great success. Coca-Cola used special beverage vending machines that produced not only beverages but also other gift vouchers to customers such as skateboards.
Direct marketing strategy, in which sellers communicate directly with consumers via emails, text messages, online adverts and even promotional letters, is affordable and has a high response rate, unlike mass, viral and guerrilla marketing strategies.
Additionally, direct marketing together with the call-to-action marketing strategy is effective in converting prospects to customers by providing links in emails and on websites or asking a prospect to call a toll-free phone number.
Quiz:
How many times have you found yourself on a web page because you clicked on a link either in your email or on a website advertising a particular product?
Many businesses prefer using the direct marketing strategy because its results can be measured directly, unlike mass marketing. However, many customers have expressed concerns over the privacy of promotional spam emails, along with environmental implications of the large volumes of published materials that marketers send them.
The close-range marketing strategy, which involves the use of wireless communication such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies, together with other online-based marketing strategies is valuable to businesses targeting tech-savvy consumers.
Call-to-action marketing strategy and close range marketing are very successful in arousing customer interest and providing businesses with useful market information. Both close-range and call-to-action marketing strategies appeal to technology-oriented customers. However, online marketing is cheaper than the two and as in the case of the methods mentioned above, targets tech-savvy people. Moreover, the high response rate and feedback relay of online marketing make the method preferable over the close range and call to action marketing strategies.
Relationship marketing strategy is suitable for organisations focused on influencing consumers to have a long-lasting emotional connection to their brands, which is crucial to business sustenance. Relationship strategy is good for businesses selling high-end products as it enables the business to connect with its customers and maintain their loyalty.
On the other hand, the transactional marketing strategy focuses on short-term goals such as customer acquisition and increasing individual sales. For example, the Coca-Cola company intends to have its customers emotionally attached to its products so that they can keep coming back to buy more. Relationship marketing strategy is fit for businesses that want to foster such a consumer brand loyalty.
The transactional marketing strategy has a return on investment in the short-run while the relationship marketing strategy’s benefits are experienced in the long-run.
Besides, niche marketing strategy, which concentrates its marketing efforts on given market segments has a strong linkage with the relationship marketing strategy and has been recommended as a suitable marketing strategy when used alongside the relationship marketing strategy (Shani & Chalasani, 1992).
Both relationship and niche marketing strategies are related to each other in that they focus on low sales and high prices. For instance, businesses dealing with high-end brands can price their products expensively and still maintain their loyal customers. The relationship marketing strategy is employed to convert customers into loyal brand lovers.
Cause-marketing strategy, in which a business aligns its brand with a cause to create brand awareness, generate profit and socially benefit those fighting for the cause, is a widely-employed marketing strategy.
Cause marketing is also a good strategy for organisations that sell products directly to consumers. Through cause marketing, a company can increase its brand loyalty by making customers feel like they are making a difference when buying a product that supports a good cause in their society.
Need Help With Your Business Studies?
If you need assistance writing a business report, our academic report writing service can provide valuable assistance.
See how our Report Writing Service can help today!
5.0 Marketing Methods and Concepts
In this chapter, the various types of marketing concepts and techniques will be discussed and evaluated on their usefulness in many business situations.
5.1 Marketing Concepts
A marketing concept is a management philosophy that determines the marketing tools to be used in achieving marketing goals through identification and satisfaction of customer needs.
5.1.1 Production concept
The production concept, which prevailed in the early twentieth century, focused on business operations. The production concept assumes that consumers prefer readily available and inexpensive goods. Accordingly, in this concept, management focused on high production levels to increase efficiency, lower costs of production and have mass distribution.
Companies that use the production concept have continual steady sales volume together with the availability of their products in many locations for their customers. Moreover, low production costs enable firms using the production concept to use competitive pricing models.
However, with poor control systems, mass production negatively affects the quality of the goods, which in turn has an adverse impact on consumer loyalty and brand strength.
The production concept is best suited for firms involved in the overseas production with the aim of reducing production costs while producing enough goods to satisfy customer demand in the market. It is also suitable for organisations delivering standardised goods that require minimal or no variation.
Illustration
During the early twentieth century, when the mechanisation of factories was starting, manufacturers such as Ford intensified the production of vehicles in a bid to reduce overall production costs while increasing output drastically. Firms could not afford stoppage of the production line, claiming it would increase the production costs by causing delays. The production concept however overlooked the product quality. Such manufacturers would produce a lot of units, but the percentage of defects was also high. Even though the units produced were cheap, they did not satisfy the needs of consumers resulting in higher external quality control costs. Quality costs are costs incurred in correcting a defect in a product that has already left the production floor. Production concept was utilised by firms involved in direct marketing together with viral marketing.
5.1.2 Selling concept
The selling concept philosophy states that businesses have to aggressively market their products through personal selling, advertisements, sales promotions and good public relations, among others, to increase consumer demand. The concept argues that in case no promotional information is passed to consumers, they are unlikely to buy large quantities of company products.
Quiz:
What product or service have you acquired in the recent past that a result of marketing carried out by its supplier?
State ten products that require the selling concept for them to be sold
The selling concept helps firms to exhaust unnecessary inventories, which in turn ensures that the flow of resources in and out of a firm is uninterrupted. However, the concept’s focus on making sales undermines activities aiming to build long term company-consumer relationships pointing to low loyalty levels among consumers.
The selling concept is suitable for businesses dealing in goods that are not highly sought after and that have numerous alternatives, for instance, insurance products. Moreover, the concept is highly applicable to organisations whose supply exceeds the demand in the market.
5.1.3 Product concept
In the product concept, customers are assumed to desire products of higher quality, better performance and superior features. Therefore, in this concept, customers are likely to purchase innovative and feature-rich products that have numerous applications.
A major advantage of products of a high quality and superior specifications is that they can sell without much focus on consumer awareness. Furthermore, marketers do not need to carry out extensive research on the targeted audience.
A good example is Apple, which, rather than depending on market needs, innovatively shapes market tastes for various technological products, for instance, smartphones. The product concept is suitable for businesses involved in the production of electronic products such as mobile phones, computers, refrigerators and other electronic components.
5.1.4 Marketing concept
In the marketing concept, firms have to study the market well to be able to satisfy consumers better than their competitors.
Firms can produce quality products that fulfil the requirements of consumers hence no wastages in terms of excess inventory.
Satisfied customers become brand ambassadors; hence businesses that focus on satisfying the needs of their consumers grow their sales and profits.
The main challenge with the marketing concept is identifying the ever-changing market tastes and preferences. Difficulty in recognising consumer needs makes it considerably difficult for businesses to satisfy customers and to establish a strong brand loyalty.
The marketing concept is suitable for organisations in the fast-moving goods industry such as fries, snacks and burgers because of the wide variances in the needs and wants of the consumers.
5.1.5 Societal concept
In the societal marketing concept, firms determine the needs and wants of customers and supply products that satisfy consumer needs, as well as their social well-being.
Socially responsible firms that satisfy customers while also caring about their society establish a good public image. Consumers are much willing to purchase products of businesses they perceive as concerned about their social well-being.
A major drawback of using the societal concept is ambiguity in that customers have a wide range of challenges, and there is no given technique that can fully address societal difficulties.
The societal concept is suitable for organisations that align their brands with a social cause with the aim of raising its brand awareness and customer loyalty while also ensuring that the society benefits from the cause.
Over the past decade, many corporations have relocated their production plants to China in a bid to cut down production costs and increase production volumes. Can you identify which marketing philosophy is the cause of this trend?
Now, can you identify other market trends that are a result of the wide adoption of the marketing concepts by businesses?
Hint: market trends can be;
- a change in the way companies view their customers
- a change in how businesses try to match customer demand and customer specifications
Discuss how the different marketing concepts contribute towards the development of marketing plans implemented by organisations.
5.2 Marketing Methods
5.2.1 Advertising
Advertising is a form of audio and visual marketing communication which involves presenting strategic messages to the market audience to promote a product or service. Advertisements are transmitted through various mass media channels such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio and websites.
Through advertisements, useful information about products that are in the market, and especially new products, is relayed to consumers. Market information provided ranges from price, functionality, quantity and other product specifications that consumers require to make good purchasing decisions.
Advertisements stimulate consumers to buy goods, hence enabling an increment in the sales of the involved firm. In addition, advertising helps businesses to remain competitive.
Need Help With Your Business Studies?
If you need assistance writing a business report, our academic report writing service can provide valuable assistance.
See how our Report Writing Service can help today!
However, to place advertisements on various media channels, high costs are involved. Huge costs can be a financial burden to small businesses.
Marketers can also provide misleading information to sway consumer thinking. Moreover, some advertisements may be inappropriate to certain age groups such as children.
Advertisements are suitable for businesses entering a new market, and that want to create awareness of their new product. The method is also fit for businesses intending to reach a large audience.
Advertising compliments the messages delivered to customers by salespeople as the consumers will not doubt the validity of the marketers.
Quiz:
Estimate the number of advertisements you watch on your television in a single day and the amount of information you receive from those advertisements that is relevant in making your purchasing decisions. (Some information may not be very helpful)
Give an example of market information you got from an advertisement that influenced a purchase you made
5.2.2 Promotion
Promotion is one of the four elements of the marketing mix. Promotion raises the customer awareness of a product, service or brand. Furthermore, promotion achieves all these objectives by presenting product information to customers, increasing demand and differentiating a given product from other products in the market.
Organisations, through promotional activities, position their products as superior in the minds of consumers. In addition, through media channels such as television, billboards and newspapers, promotion can improve brand awareness by sending out a brand’s message clearly to the target audience.
Promotional activities can trigger regular customers to inform their friends of a firm’s new product through word-of-mouth. Multi-level marketing carried out by delighted customers creates demand, which drives up the sales of a firm.
Customers get suspicious of products they think have been exaggerated in promotions resulting in the creation of a negative image about the product in their minds.
Excessive demand is also a likely result of doing promotions and in such cases, should a firm fail to satisfy the demand, the consumer's trust will be negatively impacted.
Promotions are very useful to companies with slow-moving products such as insurance covers because the marketing method helps trigger demand and creates a continuous flow of inventory.
Quiz:
Have you ever participated in any promotional activity? And what were you promoting and to what target audience?
5.2.3 Packaging
Packaging is the process of designing and producing materials that are used to cover or enclose products for distribution, storage and sale. Packaging plays several roles in the marketing of goods. The roles include protecting products during shipment, branding and including regulatory information, for instance, ingredients.
Packaging helps firms to draw consumers. The process achieves that by enabling the development of packages with intricate designs and that can be spotted easily and readily linked to the manufacturing company.
Packaging is essential in extending the shelf life of sensitive goods such as foodstuffs. Some packages maintain the enclosed to suitable atmospheric conditions. Moreover, creative packaging by a company helps to increase the brand loyalty of consumers.
However, packaging can be bulky, environmentally hazardous and expensive.
Packaging is important for all businesses.
Quiz:
Can you remember of a product you picked from a shelf because its packaging was attractive (colourful, good shape, or made of good material)?
5.2.4 Branding
Branding is a marketing method involving the conception of a name, symbol, slogan, design or a mixture of these components that identify and separate products from others.
A good branding strategy provides a firm with an advantage in competitive markets.
Organisations need to continuously conduct research, define and build their brands because of the high value it adds to business. A good brand will emotionally connect customers with the products and services of a company, motivates buyers to purchase goods and services, guarantees consumers about the quality of service they are to receive and enhances the consumers’ loyalty.
A major disadvantage is that a negative event can damage a company’s whole image and brand within a short period. A business whose image and brand have been negatively affected must build an entirely new brand to try and regain its place in the market.
Example
The recent widespread explosion of Samsung Galaxy Note 7 phones has significantly damaged the image and reputation of the Samsung Corporation even though it has other well-functioning products in the market.
Organisations that produce goods with close substitutes in a market will find branding useful in positioning its products as superior to those of rivals. With branding, a business can differentiate its products from those of its competitors to realise consistent sales volumes.
5.2.5 Public Relations
Public relations involves the effective management of information transmitted by a business when interacting with the public in a bid to shape how the general public views the involved company. Articles about a firm, events and press releases are some of the most appropriate methods of nurturing good relations between an organisation and its key publics.
Organisations do not pay media outlets for the publicity created when stories about them are aired, and this is unlike advertisements, in which involved firms incur huge costs to promote their company visibility or products. Public relations has the aspect of longevity, which makes it a better method of building a brand and image.
Publicity can reach a colossal audience through the media. The public’s view of the media as an objective third party raises the credibility of such publicity.
Businesses have no control over the type of publicity they receive from media outlets. The publicity can be positive or negative depending on the media story.
Companies facing major crises can use public relations to help salvage the damage on their brand and image. Public relations is a suitable marketing option for businesses creating awareness of a product that is being re-launched in the market.
Think of ten products or services you paid for recently and state against each product or service the marketing methods that influenced your buying decision.
Following the widespread explosion of Samsung's newly-released phones, what marketing techniques can the company employ to enable it to achieve the following:
- Rebuild their brand and public image
- Regain its lost market share
- Remove doubt in consumers that its other products are fit for use
- Drive the sales of the remaining products in its portfolio
6.0 Summary
Over the last few decades, marketing has emerged as the generation of demand rather than making consumers pay for products by focusing on identifying and satisfying their needs.
We have looked at various marketing strategies, methods and concepts that apply to all kinds of marketing situations that businesses might face. We have also compared and contrasted various marketing theories that help a marketing function and the whole business management in deciding on the marketing strategies, concept and methods to use in achieving its marketing objectives.
We have also deliberated on the importance of marketing in the success of modern organisations and critically analysed how various marketing strategies, concepts and methods are appropriate to the unique business situations that firms might encounter.
Over time, most businesses have come up with criteria for evaluating the success of marketing strategies and methods. Besides, businesses have also developed unique combinations of marketing approaches and strategies that help them to achieve their goals. New marketing plans and methods are cropping up because of the use of crude combinations of concepts and marketing strategies by businesses. The marketing function in a business plays a paramount role in ensuring the success of an organisation.
Recommended Text Books
Ferrell, O.C. and Hartline, M., 2012. Marketing strategy, text and cases. Toronto: Nelson Education.
Jobber, D. and Ellis-Chadwick, F., 2012. Principles and practice of marketing (No. 7th). New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
References
Hise, R.T. and Strawser, R.H., 2013. Application of Capital Budgeting Techniques to Marketing Operations. Readings in Managerial Economics: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social Studies, p.419.
Hultén, B., 2011. Sensory marketing: the multi-sensory brand-experience concept. European Business Review, 23(3), pp.256-273.
Nufer, G., 2013. Guerrilla Marketing-Innovative or Parasitic Marketing?. Modern Economy, 4(9A), p.1.
Shani, D. and Chalasani, S., 1992. Exploiting niches using relationship marketing. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 9(3), pp. 33-42
Cite This Module
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
 GBR
GBR 







